Search by posts
Product category
Industry News
 By Admin
By Admin
Plastic Pipes Decoded: PVC vs. PE — A Comparative Guide to Material Properties, Installation, and Best-Use Applications
Introduction to PVC and PE Pipes
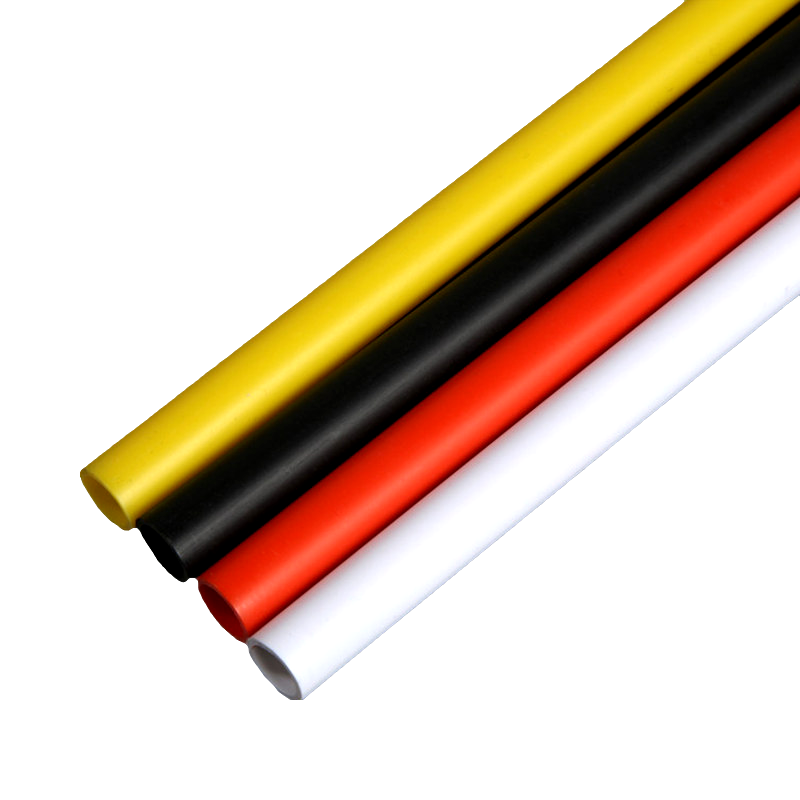
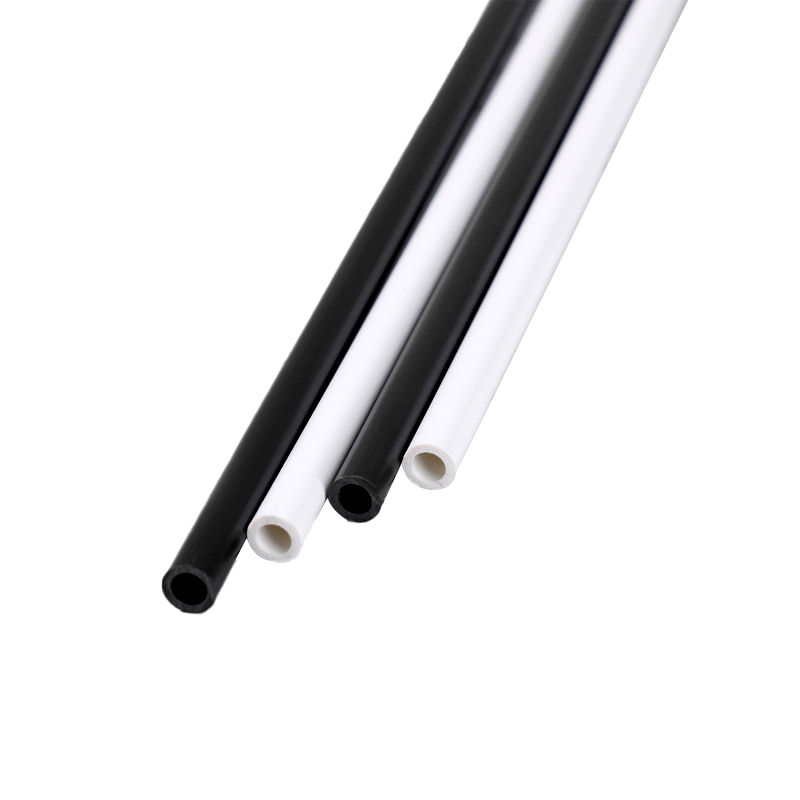
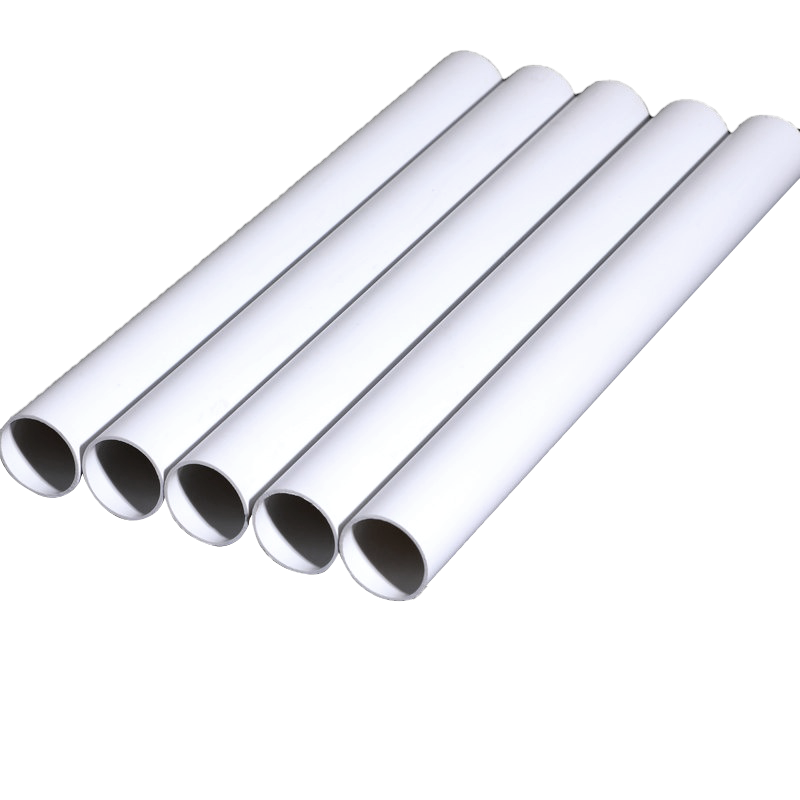
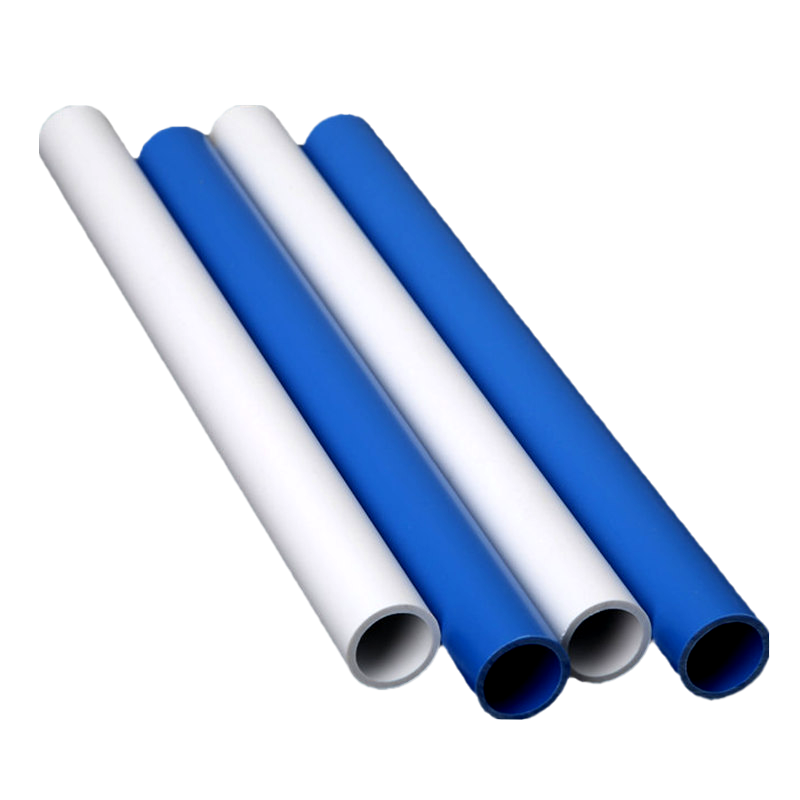
Plastic pipes are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications due to their durability, light weight, and resistance to corrosion. Among the most common types are PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes and PE (Polyethylene) pipes. Understanding their differences is essential for selecting the right pipe for specific projects, ensuring long-term performance and cost-effectiveness.
Material Composition
PVC pipes are made from polyvinyl chloride, a rigid and chemically resistant thermoplastic. PE pipes are made from polyethylene, which is flexible and more impact-resistant. The fundamental difference in material properties leads to variations in flexibility, strength, and application.
PVC Pipe Properties
PVC pipes are rigid and maintain their shape under high pressure. They resist corrosion from acids, alkalis, and salts, making them ideal for water supply and drainage systems. PVC is less flexible, which may require additional fittings for turns and bends.
PE Pipe Properties
PE pipes are highly flexible and can bend without cracking, which reduces the need for joints and fittings. They are resistant to impact and low temperatures, making them suitable for outdoor installation and underground applications. PE’s flexibility also allows better handling during transportation and installation.
Durability and Longevity
Durability is a key factor in choosing between PVC and PE pipes. Both materials are resistant to corrosion and chemicals, but their performance varies under different environmental conditions.
PVC Pipe Durability
PVC pipes have excellent resistance to chemicals and do not rust or corrode. They are ideal for indoor plumbing and pressure applications but may become brittle over time if exposed to prolonged sunlight or extreme cold without proper protection.
PE Pipe Durability
PE pipes are extremely durable in both underground and above-ground installations. They maintain flexibility in cold climates and are resistant to cracking from impact. UV-stabilized PE pipes can also withstand outdoor exposure for extended periods.
Installation and Handling
Installation methods and handling requirements differ significantly due to the material properties of PVC and PE pipes.
PVC Installation
PVC pipes require careful alignment and use of solvent cement or mechanical fittings. They are relatively easy to cut and join, but their rigidity requires precise measurements, especially in complex layouts. PVC pipes may need support brackets for horizontal runs to prevent sagging.
PE Installation
PE pipes can be installed using heat fusion or mechanical fittings. Their flexibility allows for long continuous runs with fewer joints. PE pipes can be bent around obstacles without additional fittings, reducing labor and material costs. Handling is easier due to their lightweight and impact resistance.
Applications and Suitability
Choosing between PVC and PE pipes depends on the specific application, pressure requirements, and environmental conditions.
PVC Applications
- Indoor water supply systems
- Drainage and sewer systems
- Irrigation systems with moderate pressure
- Ventilation ducts and electrical conduits
PE Applications
- Underground water supply lines
- Gas pipelines and industrial chemical transport
- Outdoor irrigation systems
- Cold climate or frost-prone installations
Comparison Table: PVC vs PE Pipes
| Feature | PVC Pipe | PE Pipe |
| Flexibility | Rigid, requires fittings for bends | Highly flexible, fewer fittings needed |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Very good |
| Durability | Moderate to high | High, impact resistant |
| UV Resistance | Needs protection | UV-stabilized versions available |
| Temperature Tolerance | Moderate, brittle in cold | Excellent, maintains flexibility |
Conclusion
PVC and PE pipes each have unique properties that make them suitable for different applications. PVC pipes are ideal for indoor plumbing, drainage, and applications requiring rigidity, while PE pipes excel in underground installations, flexible layouts, and impact-resistant environments. Selecting the appropriate pipe type depends on installation conditions, pressure requirements, and long-term durability needs.

Recommended products
-
2023 New Cheap Plastic Pipe Multiple Colors And Sizes Custom Hand Waving Flagpole
-
Wholesale Custom Pvc Material Indoor Desktop Flagpole Hand Waving Flagpole
-
Customizable Size Custom Logo Plastics Hand Waving Flagpole Big Pvc Flagpole
-
Plastics Hand Waving Flagpole Factory Direct Custom Wholesale PVC Flagpole Parts Pipe
-
Custom Easy Install Safety Flagpole Pvc China Factory Hand Waving Flagpole
-
New Popular Product Transparent Pvc Flagpole Custom Size Hand Waving Flagpole
-
2023 High Quality Hand Waving Flagpole Big Or Small Flagpole Size Custom
-
Fast Delivery Promotion Factory Wholesale Flagpole Pvc Pipe Hand Waving Flagpole
-
2023 Personalized Custom Desk Hand Waving Flagpole Outdoor White Flagpole
-
Wholesale 2023 Hot Sale Used Flagpole Weight Custom Pvc Hand Waving Flagpole
-
Wholesale Products Cheap High Quality Hand Waving Flagpole Newest Sections Flagpole
-
Wholesale Cheap High-Quality Hot Sale Flagpole Cylindrical Hand Waving Flagpole
 +86-0573-88528475
+86-0573-88528475 English
English русский
русский